The JavaScript string methods help to work on strings. JavaScript methods and properties help to work with primitive values. Following are some methods that are used to work with strings in JavaScript.
String Length
To check the length of a string in JavaScript the length property is used:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script> let a = "TutorialsArt"; document.write(a.length); </script> </body> </html>
Output:

Converting to Upper and Lower Case
A string can be converted into the upper and lower case using two methods. The toUpperCase() is used to convert a string into uppercase and toLowerCase()is used to convert a string into lowercase.
The concat() Method
The concat() method is used to join two or more strings:
String.trim() Method
The trim() method is used to remove whitespace from both sides of a string:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script> let a = " Tutorials Art "; document.write(a.trim()); </script> </body> </html>
Output:

Extraction of String Parts
Following are some methods used for extracting string parts in JavaScript:
1. The slice() Method
The slice() method is used to extract a part of the string and return it as a new string. It takes the start and ending position (end not included) as a parameter. The starting point starts from 0.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script> let s = "Python, R, C++"; document.write(s.slice(5, 9)); </script> </body> </html>
Output:

We can also apply negative slicing on a string, then the position is counted from the end of the string.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script> let s = "Python, R, C++"; document.write(s.slice(-9, -2)); </script> </body> </html>
Output:

If we skip the ending position, it will return the rest of the string.
2. The substring() Method
The substring() method is the same as slice() method but negative indexing is not allowed in this method.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script> let s = "Python, R, C++"; document.write(s.substring (7, 9)); </script> </body> </html>
Output:

If we skip the ending position, it will return the rest of the string.
3. The substr() Method
The substr() method is the same as slice() method but the second parameter specifies the length of the extracted part.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script> let s = "Python, R, C++"; s. substr (7, 9) document.write(s.substr (7, 9)); </script> </body> </html>
Output:

If we skip the ending position, it will return the rest of the string and in case of negative indexing, it will start from the end of the string.
String Content Replacement
To replace a specific value with another string value the replace() method is used. It does not replace the original string and return a new string with replaced value.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
let a = "Welcome to website!";
let b = a.replace("website", "Tutorials Art");
document.write(b);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

If the replacement word is available much time in the original string then it will replace only the first match by default.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
let a = "Welcome to website and website!";
let b = a.replace("website", "Tutorials Art");
document.write(b);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
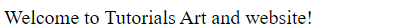
The replace() method is case-sensitive by default. Writing WEBSITE (with upper-case) will not work. To replace case insensitive, use a regular expression with an /i flag (insensitive):
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
let a = "Welcome to website and website!";
let b = a.replace("website", "Tutorials Art");
document.write(b);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
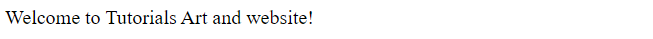
To replace all matches, use /g flag instead of /i flag.
Padding String
ECMAScript 2017 used two new String methods padStart and padEnd to support padding at the start and end of a string.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="tacode1"></p>
<p id="tacode2"></p>
<script>
let a = "8";
document.getElementById("tacode1").innerHTML = a.padStart(3,0);
document.getElementById("tacode2").innerHTML = a.padEnd(3,0);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

String Characters Extraction
There are 3 methods for extracting string characters:
1. Property Access
The ECMAScript 5 (2009) allows property access [ ] on strings:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script> let a = "Tutorials Art"; document.write(a[1]); </script> </body> </html>
Output:

2. The charAt() Method
The charAt() method is used to returns the character at a specified index in a string:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script> let a = "Tutorials Art"; document.write(a.charAt(1)); </script> </body> </html>
Output:

3. The charCodeAt() Method
The charCodeAt() method is used to return the Unicode of the character at a specified index in a string:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <script> let a = "Tutorials Art"; document.write(a.charCodeAt(1)); </script> </body> </html>
Output:

Converting a String to an Array
Using the split() method we can convert a string into an array.
Following browsers support for JavaScript string padding:
| Chrome 57 | Edge 15 | Firefox 48 | Safari 10 | Opera 44 |
| Mar 2017 | Apr 2017 | Aug 2016 | Sep 2016 | Mar 2017 |
