This chapter explains how to make input fields required and, if necessary, provide error messages.
PHP Form Required Fields
Let’s look at a PHP for fields, some of which cannot be left blank and must be filled out:
| Field | Validation Rules |
| Name | Required+ It can only contain letters and whitespaces. |
| Required. + Must contain a valid email address (with @ and .) | |
| Gender | Required + Must select from the given option. |
| Comment | Optional – Multiple line text. |
Now, let’s look at an example to see how we can make the above fields mandatory, and then we’ll talk about how the code works.
<?php
// Variable declaration and setting default value null
$nameError = $emailError = $genderError = "";
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
if (empty($_POST["name"])) {
$nameError = "Name is required";
} else {
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["email"])) {
$emailError = "Email is required";
} else {
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["gender"])) {
$genderError = "Gender is required";
} else {
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["comment"])) {
$comment = "";
} else {
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
}
}
?>We’ve added several additional variables to the above code: $nameError, $emailError, and $genderError. The required fields error messages will be stored in these error variables. For each $_POST variable, we’ve added an if else expression. This uses the PHP empty() method to see if the $_POST variable is empty.
If the required field empty, an error message is saved in the various error variables; if it’s not empty, the test_input() function gives the user input data:
Let’s take a look at how we may display these error messages that we defined earlier:
PHP – Display The Error Messages
Then, we put a script after each required field in the HTML form that generates the proper error message if the user tries to submit the form without filling out all required data.
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.error {color: #FF0000;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<?php
// Variable declaration and setting default value null
$nameError = $emailError = $genderError = "";
$name = $email = $gender = $comment = "";
if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
if (empty($_POST["name"])) {
$nameError = "Name is required";
} else {
$name = test_input($_POST["name"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["email"])) {
$emailError = "Email is required";
} else {
$email = test_input($_POST["email"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["gender"])) {
$genderError = "Gender is required";
} else {
$gender = test_input($_POST["gender"]);
}
if (empty($_POST["comment"])) {
$comment = "";
} else {
$comment = test_input($_POST["comment"]);
}
}
function test_input($data) {
$data = trim($data);
$data = stripslashes($data);
$data = htmlspecialchars($data);
return $data;
}
?>
<h2>PHP Form Validation Example</h2>
<p><span class="error">* required field</span></p>
<form method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">
Name: <input type="text" name="name">
<span class="error">* <?php echo $nameError;?></span>
<br><br>
E-mail: <input type="text" name="email">
<span class="error">* <?php echo $emailError;?></span>
<br><br>
Gender:
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female">Female
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male">Male
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="other">Other
<span class="error">* <?php echo $genderErr;?></span>
<br><br>
Comment: <textarea name="comment" rows="5" cols="40"></textarea>
<br><br>
<input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<?php
echo "<h2>Your Input:</h2>";
echo $name;
echo "<br>";
echo $email;
echo "<br>";
echo $gender;
echo "<br>";
echo $comment;
?>
</body>
</html>
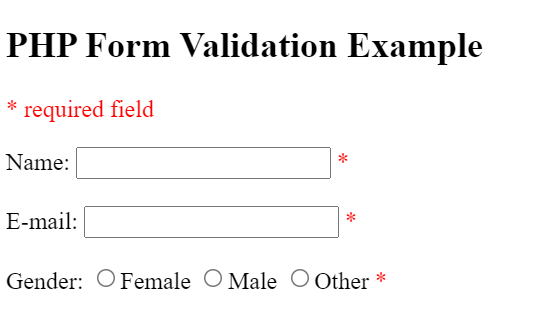
This is how the required fields will look like: