The bar chart in R uses rectangular bars to visualize the data. The height of the bars is proportional to the values they represent. The bar charts can be displayed either horizontally or vertically.
By using the barplot() function a vertical bar chart is drawn:
# x-axis values
x <- c("Python", "R", "Java", "C++", "Ruby")
# y-axis values
y <- c(34,65,54,58,32)
barplot(y, names.arg = x)
Output
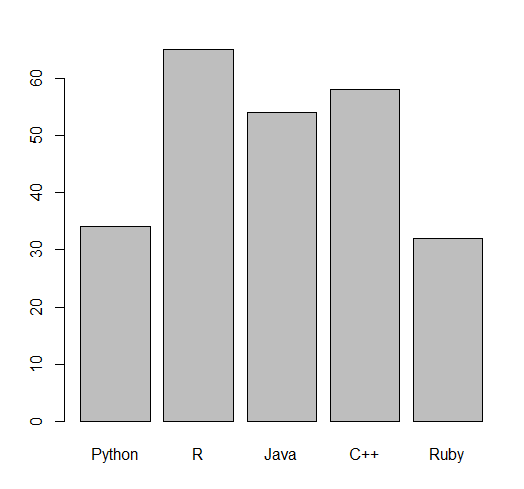
The above example shows:
- The
xvariable represents values in the x-axis (“Python”, “R”, “Java”, “C++”, “Ruby”) - The
yvariable represents values in the y-axis (34,65,54,58,32) - The
barplot()function is use to create a bar chart of the values names.argdefines the names of each observation in the x-axis
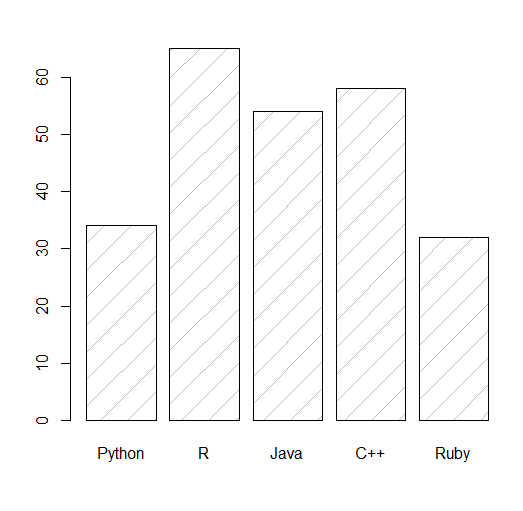
Density Bar Chart in R
The density parameter can be used to change the bar texture.
x <- c("Python", "R", "Java", "C++", "Ruby")
y <- c(34,65,54,58,32)
barplot(y, names.arg = x, density = 5)
Output
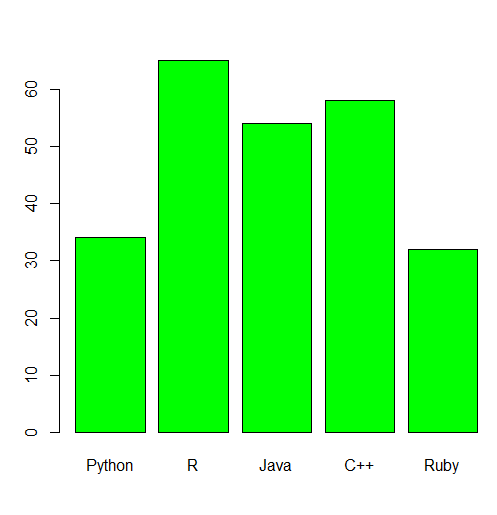
Bar Color
To change the color of the bar you can use the col parameter.
x <- c("Python", "R", "Java", "C++", "Ruby")
y <- c(34,65,54,58,32)
barplot(y, names.arg = x, col = "green")
Output
Bar Width
To change the width of the bar, you can use the width parameter.
x <- c("Python", "R", "Java", "C++", "Ruby")
y <- c(34,65,54,58,32)
barplot(y, names.arg = x, width = c(1,2,3,4,5))
Output
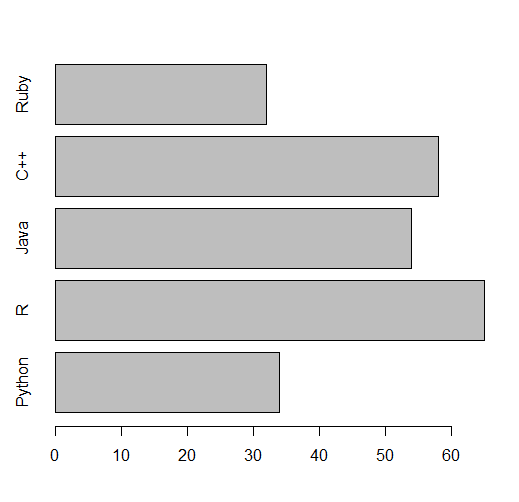
Horizontal Bars
The bars can be displayed horizontally instead of vertically by using horiz=TRUE:
x <- c("Python", "R", "Java", "C++", "Ruby")
y <- c(34,65,54,58,32)
barplot(y, names.arg = x, horiz = TRUE)
Output